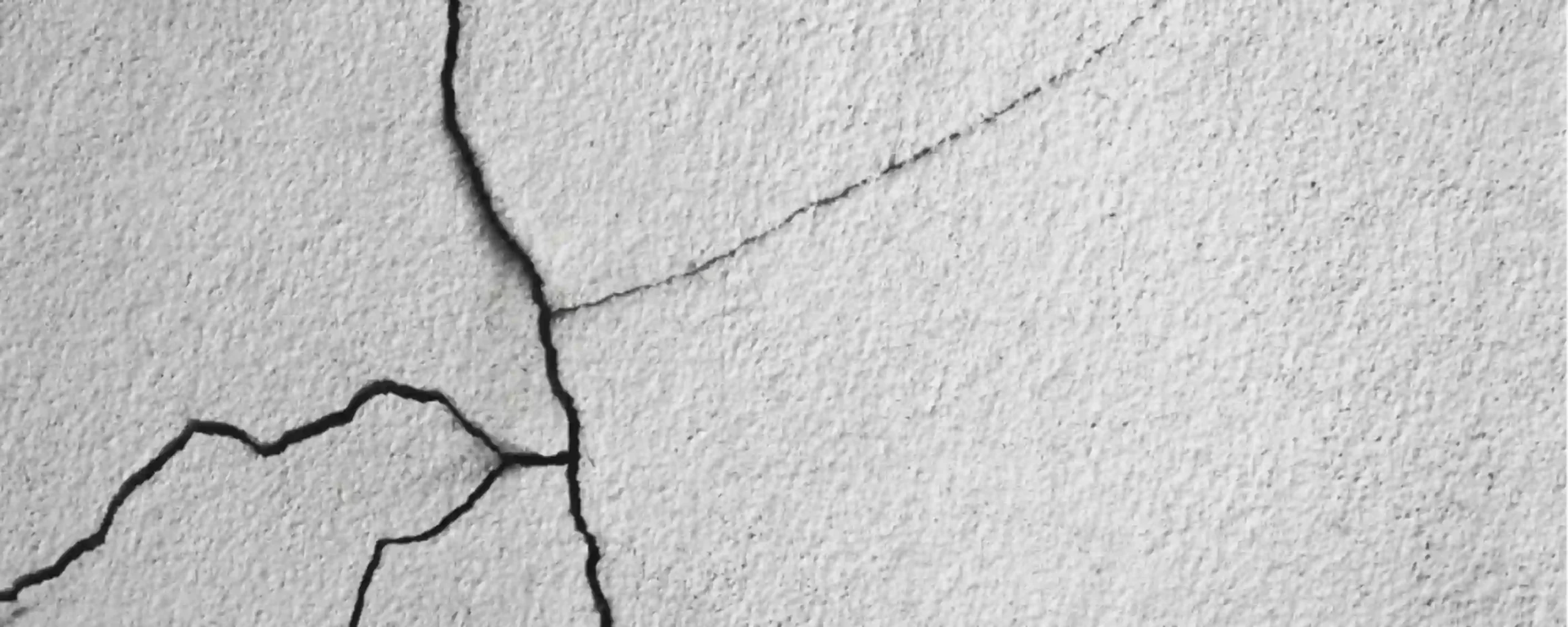
What causes cracks in the walls? There are several reasons for cracks in walls. For example, structural issues are caused by the contraction and extraction of the materials used in construction. Or simply a minor problem, which includes hairline cracks. These can be fixed by using fillers and paints. These cracks are a result of temperature change and moisture content. Various types of cracks can occur.
- 1 Types of Cracks
- 2 Reasons for Cracks in Walls:
- 2.1 Foundation Settlement
- 2.2 Thermal Expansion and Contraction
- 2.3 Moisture Infiltration
- 2.4 Poor Construction Practices
- 2.5 Soil Shrinkage
- 2.6 Vibration and External Forces
- 2.7 Load Bearing Issues
- 2.8 Seismic Activity
- 2.9 Improper Curing of Concrete
- 2.10 Plumbing Leaks
- 2.11 Lack of Maintenance
- 2.12 Structural Overloading
- 2.13 Overloading of Floors
- 2.14 Wind Loads
- 2.15 Differential Thermal Movement
- 2.16 Chemical Reaction
- 2.17 Poor Installation of Doors and Windows
- 2.18 Inadequate Waterproofing
- 3 Effect of Cracks in the Walls
- 4 Conclusion
Types of Cracks

Vertical Cracks
Vertical cracks are typically straight hairline cracks, though they can become slightly wider. Concrete must be prepared using the proper techniques and materials to avoid this.
Causes of vertical crack:
- When plaster expands during drying, it can lead to shrinkage. This is due to humid conditions. This can be fixed using paint and filling.
- Vertical cracks are also caused by foundation settling. This is due to the soil movement, which can affect the support of the building. This needs serious attention.
- The seasonal changes can cause the soil to expand and contract. It can result in flooding and lead to cracks in the walls.
Horizontal Cracks
The horizontal cracks are an indication of a wall failure. This needs proper immediate attention.
Causes of horizontal cracks:
Poor soil
Wet or dry clay-rich soil has the feature of expanding and contracting. This causes pressure on the foundation walls, which can lead to cracking.
Hydrostatic pressure
The excess water occurs due to poor drainage. This affects the foundation of the building and builds pressure. This pressure causes cracks in the foundation wall.
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction includes the corrosion of metal. It can alter the structure of the walls, causing cracks over time.
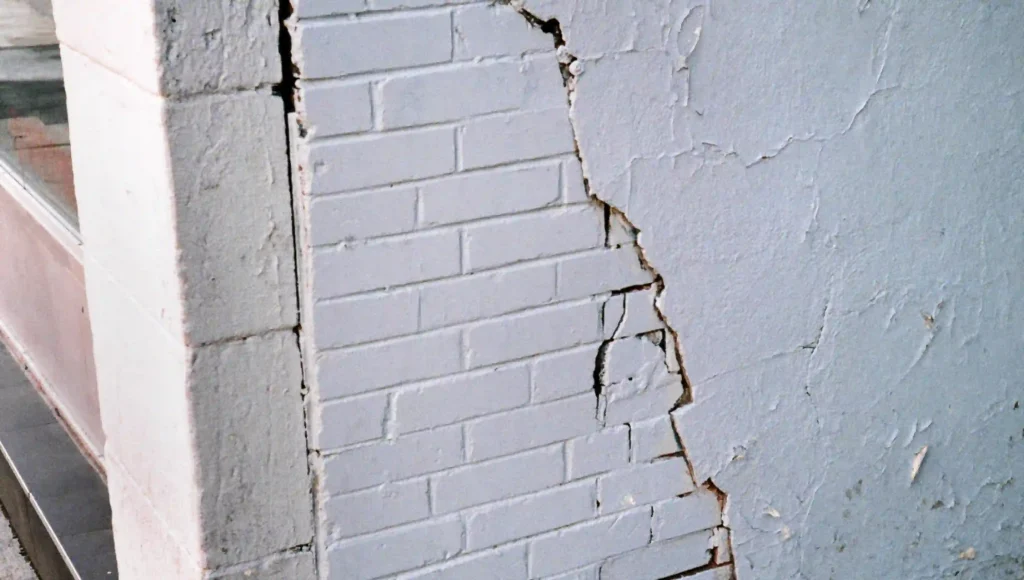
Diagonal Cracks
Diagonal cracks are often referred to as shrinkage cracks due to the concrete’s contraction during the curing process.
Causes of diagonal cracks
Structural deterioration
The diagonal cracks often occur in concrete due to concrete shrinkage. This is also called a shrinkage crack. Poor soil conditions during construction can lead to such issues over time.
Brick walls
When stress distribution is uneven in brick walls, diagonal cracks form. These are load-bearing tracks and can commonly occur near windows or doorways.
Reasons for Cracks in Walls:
Foundation Settlement
If the soil underneath a structure fails to support the building’s weight, cracks less than 1.5 mm thick may appear. Stabilizing the structure using appropriate methods can prevent these cracks. This is seen as vertical or diagonal cracks in the windows or doors.
Thermal Expansion and Contraction
Temperature variations cause thermal expansion in concrete. When there is a change in the moisture content of the air, it leads to temperature variation. Expansion or contraction occurs in these materials. Expansion is due to heat, and contraction is due to the cooling effect. This can lead to stress on the walls. Usually, hairline cracks appear in a horizontal or stair-like pattern.
Moisture Infiltration
Flow of water or moisture fluctuation can result in cracks in the building. Water flow into the building material can cause it to expand. Water intrusion can weaken material strength, and when moisture evaporates, gaps can form, leading to issues such as bulging, peeling paint, and mold growth.
Poor Construction Practices
When the materials used in the construction, like sand and cement aggregate, are poorly mixed, it causes cracks. Proper load support design, including adequate steel reinforcement, is critical; inadequate support can lead to cracks. Other factors include improper curing, low-quality materials, and poor workmanship.
Soil Shrinkage
The movement of soil can cause high stress on the foundation of the construction. Its expansion and contraction with changes in weather conditions can cause cracks in the walls.
Vibration and External Forces
Vibration caused by heavy machinery, nearby construction, and traffic can cause external forces. These forces lead to creating stress and tension on the building walls. It results in developing cracks over time.
Load Bearing Issues
The load-bearing walls, such as pillars, need adequate support. When there is an excessive strain or inadequate support, it can lead to poor load bearing. This causes cracks in where walls meet ceilings as a sign of load-bearing issues.
Seismic Activity
The regions that are prone to earthquakes affect the building. It has increased stress, which results in cracks in the walls. Buildings in such places must be designed to withstand these seismic forces.
Improper Curing of Concrete
Curing is a process that occurs in the preparation of concrete. If the concrete does not dry and harden properly, it has a high risk of developing cracks. It fails to provide the necessary strength and durability that the concrete requires.
Plumbing Leaks
Water leakage from pipes and drainage systems can cause structural damage. If water leaks between the concrete particles, it can weaken its material strength. This results in cracking of the walls.
Lack of Maintenance
Negligence and improper maintenance of construction can lead to crack occurrences. Filling the gaps and repairing smaller cracks with paint and adequate material is essential. Addressing the moisture issues will help prevent cracks.
Structural Overloading
A building must be designed according to its capacity. Overloading the construction can result in cracks in the walls. For example, shifting from residential buildings to commercial use can be inadequate.
Overloading of Floors
The excessive weight more than the building can hold leads to increased stress on the lower walls, which results in cracks. Upper floors, which are excessively weighted, cause increased pressure on the building.
Wind Loads
High winds can cause pressure on the building. Any construction near windmills or seashore can experience high tide winds. This causes increased tension on the surface of the walls. It results in introducing cracks.
Differential Thermal Movement
The expansion and contraction that occur in different buildings at different rates also experience a variation in the temperatures. The joints of the building can cause movement between the different materials used for construction.
Chemical Reaction
Chemical reactions have a severe impact on the walls of the building. The highly reactive chemicals can cause expansion and cracking of the walls. This can highly risk the building structure and its quality.
Poor Installation of Doors and Windows
Proper workmanship when installing doors and windows during construction is important. The corners of windows and doors are more prone to crack occurrence. These are places where stress is more concentrated and requires proper attention.
Inadequate Waterproofing
Always notice that the walls have adequate waterproofing. The walls are more prone to water-related damage due to moisture infiltration, which can lead to the cracking of the walls.
Effect of Cracks in the Walls
- The cracks indicate that there is structural damage, which is an underlying problem. For example, foundation problems can affect the strength of the construction.
- Visible cracks can make the building look less attractive, reducing its aesthetic value.
- Cracks in the building can also reduce the property’s market value. The reasons are an indication of poor construction. Pests in the building can also lead to cracks.
Conclusion
Understanding cracks in the wall is essential in taking safety measures and preventing the building. Identifying the cause of damage in the building. Cracks are seen in both old and new buildings. They are not different, but we must take necessary and immediate actions. This helps prevent the spread of the cracks further. Cracks may pose a serious problem. While some cracks may pose a serious risk to the structural integrity of the entire building, others may be superficial and easily remedied. Determining the crack helps in choosing the appropriate method to fix the damage.

